
Dependency injection in Symfony
You work with Symfony, but the concept of dependency injection is a little blurry for you? Find out how to take advantage of the component reading this article.

We've been talking about serverless architectures for years. But what does that mean precisely and how to develop PHP applications that can be deployed on this architecture?
Serverless architecture is a model in which the cloud service provider (although it is possible to host its own serverless infrastructure, we will come back to this) is responsible for executing a piece of code by dynamically allocating the resources.
The code is generally executed in stateless containers and can be triggered by various events (HTTP request, crons, download of a document, etc.). It usually comes in the form of a function, so serverless is sometimes called "Functions as a Service" or "FaaS".
Serverless architecture can be useful in several cases:
The first advantage is that there is no infrastructure or resource management to be carried out. You do not need to provision and upgrade the servers because the cloud provider takes care of it.
Then, you only pay for the resources you actually use, it's called Pay as you go. That is, you only pay for resources when they are being used. The containers go out if no function is called for a given time allowing you to save money.
Another advantage is the scalability of your platform. The infrastructure adapts automatically according to the load.
It's also easy to deploy new versions of your applications, which can help speed up release cycles.
In addition, this allows the team to focus on the development of the application and invest their energy and resources in its proper functioning.
Finally, not having containers that run unnecessarily helps save energy and it's better for the planet!
One of the big drawbacks that we can see is the cold start, that is to say the time that the containers take to start if they were switched off when a function was called. Currently, it varies between a few hundred milliseconds and a second. Although it depends on the language of your application and the size of your functions.
Another constraint is the maximum execution time of a function. It varies depending on cloud providers (9 minutes at Google function, 15 minutes for AWS Lambda). It must therefore be taken into account in various processes in your application.
There are also limitations related to memory, the maximum size of the packages you deploy and the available disk space. Below is an excerpt from the limitations of AWS Lambda to give you an idea.
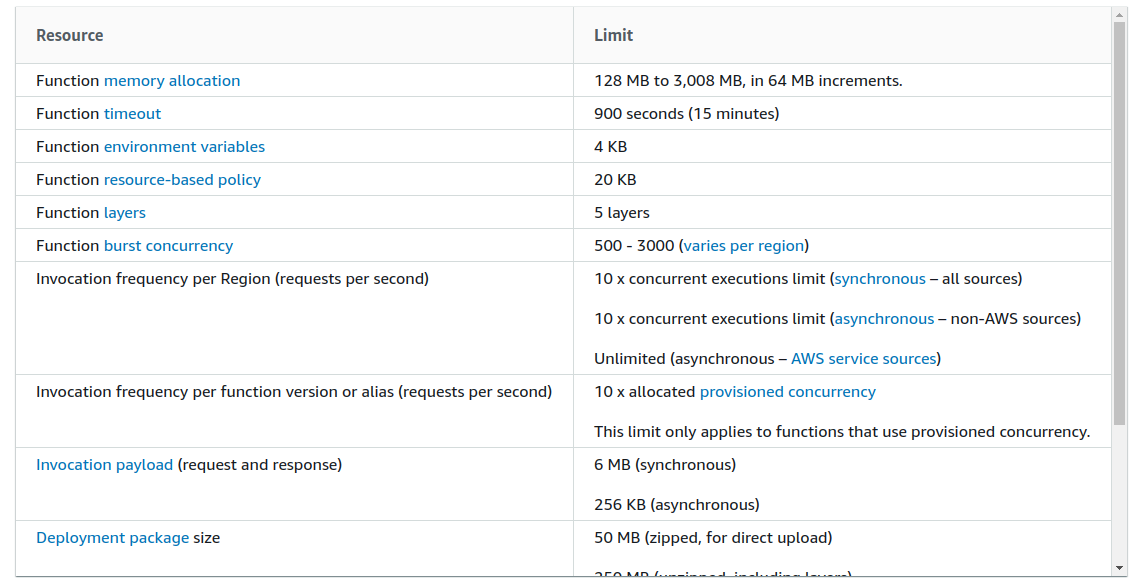
Another point to keep in mind is that the price of our infrastructure can be unpredictable. Since the cloud provider takes care of everything, we therefore have no control over how it manages resources, and in the event of an unforeseen event which places a lot of demand on our serverless functions, the price could rise. Rest assured, it is nevertheless possible to create alerts and be notified by your cloud provider if you exceed a certain amount.
A final drawback is related to testing and fixing bugs in your functions. It takes a little practice and sometimes the use of additional services, such as [AWS SAM](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/what-is -sam.html) for example.
We will now see the main cloud players for deploying PHP applications on serverless infrastructures.
Currently, it is possible to deploy PHP applications on the following cloud infrastructures:
There are several frameworks for deploying a serverless infrastructure on Kubernetes. The most famous are:
I make a special mention here to the Apache OpenWhisk platform. It is an open source project that supports PHP out of the box (among other programming languages), which is available via:
Each solution seen above comes with its own SDK that you need to familiarize yourself with. So, if you change platforms, you have to redo all the configurations and all the installations.
There is a solution that tries to make all the configurations centralized in one place and to be as platform agnostic as possible - the serverless framework.
The serverless framework includes an open source CLI which avoids the installation of multiple SDKs.
The installation of the servelss framework is very fast and simple:
$ npm install -g serverless $ serverless -v Framework Core: 1.67.3 (standalone) Plugin: 3.6.6 SDK: 2.3.0 Components: 2.29.0
The implementation and configuration of this framework in your application is done via a serverless.yml file which looks like this:
# serverless.yml service: my-service provider: name: aws runtime: nodejs12.x functions: # Your functions hello: events: # The events that trigger this function - http: get hello usersCreate: events: - http: post users / create usersDelete: events: - http: delete users / delete plugins: - serverless-offline
The serverless-offline plugin is used to emulate AWS Lambda on your machine and allows you to test your functions.
Of course, the configuration is not completely agnostic of the provider that you would have chosen, because the options strongly depend on it.
To deploy and call a function with the serverless framework we use the following commands:
$ serverless deploy -v $ serverless invoke -f hello -l
In a following article, we will see in detail how to deploy a PHP application on AWS Lambda with Bref.
Author(s)
Marie Minasyan
Astronaute Raccoon @ ElevenLabs_🚀 De retour dans la Galaxie.
You wanna know more about something in particular?
Let's plan a meeting!
Our experts answer all your questions.
Contact usDiscover other content about the same topic

You work with Symfony, but the concept of dependency injection is a little blurry for you? Find out how to take advantage of the component reading this article.

Are you suffering from domain anemia? Let's look at what an anemic domain model is and how things can change.

How to deploy PHP applications to AWS Lambda with Bref